Key Takeaways:
- Sheeting vs. Shoring: Sheeting is primarily used for soil retention and preventing soil movement, while shoring provides structural support and stability.
- Uses: Sheeting is commonly employed in deep excavations like basements, whereas shoring is crucial in trench excavations and structural repairs.
- Materials: Wood, steel, and aluminum are the most commonly used materials, each chosen based on project requirements and soil conditions.
What is Sheeting in Excavation?
In the world of excavation, ensuring the safety and stability of worksites is paramount. Sheeting and shoring are two critical techniques employed to prevent collapses and safeguard workers and equipment during excavation projects.
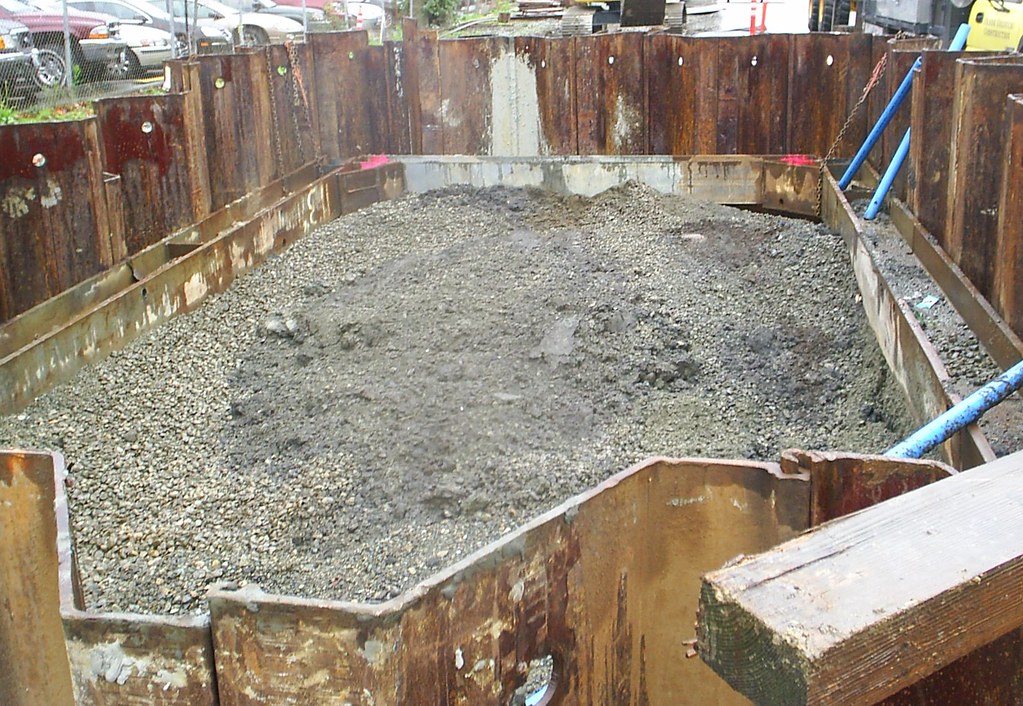
Sheeting involves driving large, flat sheets of material into the ground alongside the excavation area to support the earth’s walls. This technique is crucial for maintaining stability in excavation sites, with materials typically including wood, steel, and aluminum.
What is Shoring in Excavation?
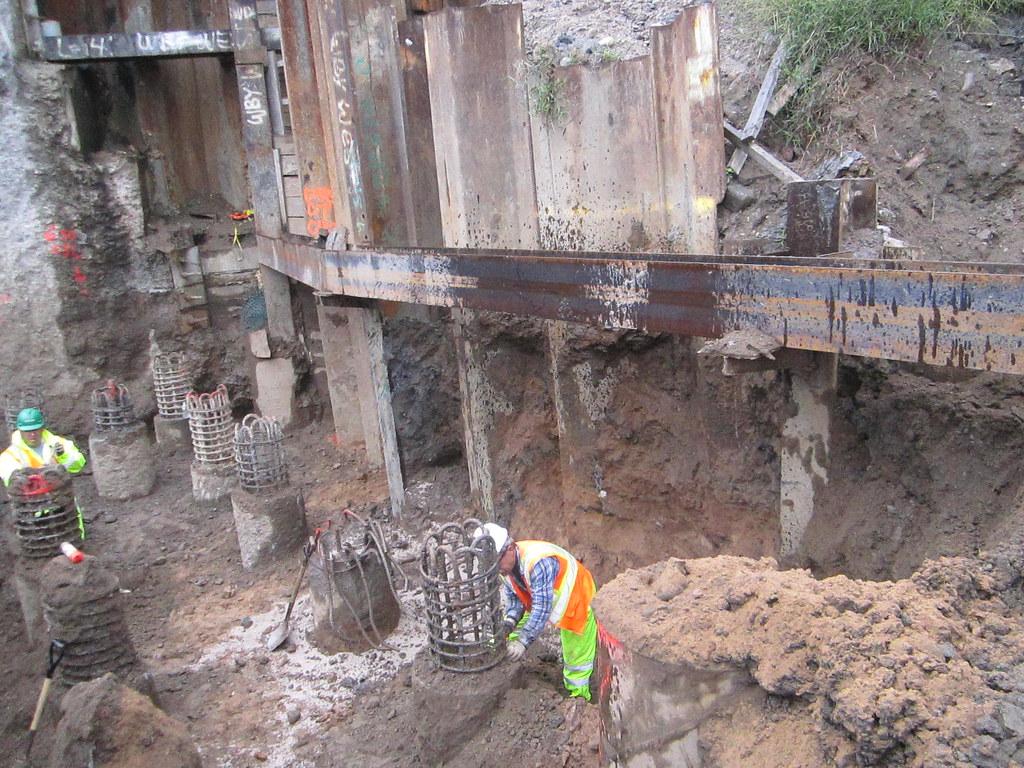
Shoring uses shores (props) to support structures, trenches, or excavations at risk of collapsing or during alterations. This method, which often employs hydraulic jacks, posts, or other mechanical systems, is essential for providing temporary support to excavation sites.
The Differences Between Sheeting and Shoring
The primary distinction between sheeting and shoring lies in their functions and applications. Sheeting focuses on retaining the earth, while shoring is geared towards supporting structures and enhancing overall stability.
Sheeting
Definition and Purpose: Sheeting refers to the process of installing a temporary or permanent barrier in an excavation to prevent the surrounding soil from collapsing. It’s primarily used to protect workers and equipment from cave-ins and to maintain the integrity of the excavation walls.
Materials Used: Common materials for sheeting include wood planks, steel sheets, and aluminum panels. The choice depends on factors like soil type, depth of the excavation, and project budget.
Installation: Sheeting is typically installed vertically into the ground, alongside the excavation walls. The method of installation can vary; it might involve driving the sheets into the ground or placing them in pre-dug trenches.
Usage Scenarios: It’s most often used in shallow excavations or trenches where there’s a risk of soil collapse but where the pressures are not excessively high.
Shoring
Definition and Purpose: Shoring is a method used to support the sides of an excavation to prevent soil movement and cave-ins. Unlike sheeting, shoring is more about structural support and can involve a range of techniques and materials.
Materials Used: Shoring systems can include hydraulic jacks, timber, steel beams, and braces. The materials and design depend on the excavation depth, soil conditions, and the expected loads.
Installation: Shoring involves setting up support structures that can either push against the walls (like hydraulic shores) or provide a framework to hold the walls in place (such as soldier beams and lagging).
Usage Scenarios: Shoring is essential in deeper excavations or in situations where the excavation walls are unstable or subject to higher pressures. It’s also crucial when working near existing structures or in urban environments where the stability of adjacent buildings is a concern.
Different Uses of Both of Them
- Purpose and Function: Sheeting is more about creating a barrier against soil collapse, while shoring is about actively supporting and stabilizing the excavation walls.
- Materials and Design: Sheeting usually involves simpler materials like planks or panels, whereas shoring can be a more complex setup with beams, braces, and hydraulic systems.
- Application Depth: Sheeting is typically sufficient for shallower excavations, whereas shoring is necessary for deeper or more complex sites.
- Installation Method: Sheeting is often directly driven into the ground, while shoring installations can be more varied and complex, often requiring detailed engineering.
Types of Material Used for Sheeting and Shoring
The selection of materials for sheeting and shoring is influenced by various factors such as project requirements and soil conditions.
Wood, steel, and aluminum are the most popular choices, each offering unique advantages depending on the specific needs of the project.
Wood
Usage in Sheeting:
- Planks and Boards: Wood is traditionally used for sheeting in the form of planks or boards. These are vertically driven into the ground or placed into pre-dug trenches along the excavation walls.
- Suitability: Ideal for shallower excavations where the pressure from the surrounding soil is not excessively high.
- Flexibility and Cost: Wood is flexible and easily cut to size, making it suitable for varying trench widths. It’s also more cost-effective compared to metal options.
Usage in Shoring:
- Timber Shoring: Involves the use of timber posts, wales, and struts to support the excavation walls. This method is more traditional and often seen in smaller or less complex projects.
- Configuration: The timber is configured in various ways, such as soldier piles with lagging, to provide adequate support.
- Application: Best for moderate depths and in situations where the soil condition is stable enough to be supported by timber.
Steel
Usage in Sheeting:
- Steel Sheeting: Often used in the form of interlocking steel sheets. These sheets are driven deep into the ground and are excellent for providing a strong, durable barrier against soil collapse.
- Heavy-Duty Applications: Ideal for deeper excavations or where there is significant soil pressure. Steel sheeting is also used in water-logged sites due to its strength and impermeability.
Usage in Shoring:
- Steel Frames and Hydraulics: Steel is used in more robust shoring systems, including hydraulic shoring and soldier beam and lagging systems.
- Soldier Beams: These are steel H-beams placed vertically into the ground at regular intervals along the trench, with horizontal supports.
- Hydraulic Shoring: Uses steel plates and hydraulic pistons to exert pressure against the trench walls to prevent collapse.
Aluminum
Usage in Sheeting:
- Lightweight Sheeting: Aluminum sheeting is less common but valued for its lightweight and ease of handling. It’s used in situations where quick installation and removal are necessary.
- Applications: Suitable for small-scale or temporary excavations, especially in urban areas or confined spaces.
Usage in Shoring:
- Aluminum Shoring Systems: Often seen in the form of lightweight shoring systems, like aluminum trench boxes or hydraulic shoring.
- Portable and Easy to Install: Ideal for situations requiring quick setup and removal. Aluminum shoring is often used in utility and maintenance work.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of sheeting and shoring is crucial for any excavation project. These techniques are integral to maintaining safety and efficiency on-site. For a company like In-Depth Excavation, with a commitment to professional, responsive, and customer-focused service, applying these methods effectively ensures that every project meets the highest standards of safety and excellence.
FAQ on Sheeting and Shoring in Excavation
The main purpose of sheeting in excavation is to provide temporary support to the walls of an excavation site, preventing soil movements and collapses. It involves driving large, flat sheets of material, such as wood, steel, or aluminum, into the ground to form a continuous wall that holds the earth in place.
Shoring is used to support structures, trenches, or excavations at risk of collapse, primarily through the use of props or supports like hydraulic jacks, posts, or mechanical systems. While sheeting is used for soil retention, shoring is more focused on providing structural support.
Sheeting is often employed in deep excavations, such as for building basements or underground facilities. Shoring is commonly used in trench excavations, infrastructure repairs, and in situations where temporary structural support is necessary.
Common materials for sheeting and shoring include wood, steel, and aluminum. The choice of material depends on the project’s specific requirements, soil conditions, and the depth of the excavation.
Yes, there are several methods of shoring, including hydraulic shoring, beam and plate shoring, and slide rail shoring. Each method has its own advantages and is selected based on the project’s needs and the conditions of the excavation site.
- Yes, the soil type can significantly influence the choice and application of sheeting and shoring techniques. Softer soils may require more robust support systems, while stable, rocky soils might need less intensive methods.
While not all excavation projects may require sheeting and shoring, they are essential for projects involving deep excavations, unstable soil, or when working near existing structures. Safety is the primary concern, and these techniques are employed to ensure the stability and safety of the excavation site.
In-Depth Excavation, with over 60 years of combined experience in the field, ensures the effectiveness of sheeting and shoring by conducting thorough site assessments, using high-quality materials, and employing skilled professionals to implement these techniques as per project requirements.